Q & A
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Questions
- What is the difference between PFSC and other methods of protein alphabetic description?
- Why choose the shape of 5 C-alpha backbone in protein as an element to describe protein folding?
- Why are 27 PFSC vectors?
- What is the neighboring relationship of 27 vector?
- What does the protein structure fingerprint include?
- What is the meaning of protein similarity score?
- What is the difference between Doking and PBSDD?
- What is the imitative data required to create protein structure fingerprint?
- What does the protein structure fingerprint include?
- How does a user create own library?
- How is the drug binding site defined?
- Why Protein Folding Structure Alignment approach provides a consistent process to compare protein structure.
- Why PFSC approach can be used to determine the secondary structure from X-ray crystal graphic data with low resolution?
- What is the format of output?
- What is new feature in Protein Folding Structure Alignment approach?
- Is the PBSDD same as the Docking?
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Answers
1. What is the difference between PFSC and other methods of protein alphabetic description?
So far, protein alphabetic methods depend on statistic approach to collect basic folding elements, and then assign letters to each element. The rare case may be omitted, and each element is isolated. The 27 PFSC vectors are obtained by restrict mathematic derivation, which is able to describe the all possible shapes of 5 residues in protein approach. It makes complete assignment for protein conformation without gap. Also, All 27 PFSC vectors have the integrated relationship, which each vector associate to its neighborhood vectors with partial similarity (Figure on right of middle). Each PFSC has its explicit characteristic in conformation.
2. Why choose the shape of 5 C-alpha backbone in protein as an element to describe protein folding?
The folding shape of 5 C-alpha backbone has two dihedral angles with 4 C-alpha overlap, which may help the folding tendency continue or reverse. Also, 4-5 C-alpha complete a cycle for alpha fragment. The element with less than 5 C-alpha does not show the folding continuity; the element with more than 5 C-alpha increases the complicity.
3. Why are 27 PFSC vectors?
With mathematic derivation, we proved that three variables could describe the folding shape of 5 connected points. In order to study the similarity, each variable has been partitioned into three ranges, which generated 27 PFSC vectors. In principle, we may partition more or less. However, results already showed that 27 PFSC is good enough to describe the protein folding conformation.
14. What is new feature in Protein Folding Structure Alignment approach?
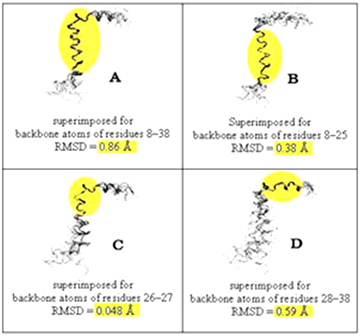
For acquisition of optimistic solutions, most of methods attempt to find out the higher number of equivalent residues with the lower RMSD through superimposition of protein 3D structures or structural fragments. Unfortunately, it is tough to optimize these two numbers simultaneously because the intention of higher number of equivalent residues leans higher RMSD, or the favor of lower RMSD leads less number of equivalent residues. Also, in order to get protein structural superimposition, two artificial factors may be justified, i.e. one is the cutoff distance for RMSD and another is the location for initiative focus. These artificial factors are not unique for various methods, and it directly affects the outcome of protein structural comparison. Below figure shows that focusing on different location gives different RMSD.
The protein folding structural alignment (PFSA) has new feature which is able to avoid to selection of artificial parameters during protein comparison process and to provide a unique measurement for various protein structure comparisons.
16. Is the PBSDD same as the Docking??
No,PBSDD is different from Docking technology.| Docking | PBSDD |
|---|---|
Evaluate a set of molecules, to found out which molecule is better fitted to the protein target. |
Screen a set of proteins, to discover which proteins are targeted by a specific molecule. |
