- Conformation Analysis
- Protein Structure Alignment
- Protein Misfolding vs. Alzheimer Disease
- Fragment Search
- Evaluate Structural Similarity for Proteins with Diverse Degrees in Homology
- Mutation Analysis
- Analysis of CDR Loops in Antibody
- Comparison of Insulin Receptor vs. IGF-1 Receptor
- Drug Binding Site
- Predicting Off Target Hits in Drug Discovery
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Evaluate Structural Similarity for Proteins with Diverse Degrees in Homology
Distribution of PFSA-Score is Coherent with Structure Classification of Protein (SCOP)

For proteins with lower homology, the structural comparison is more difficult because of the variety of topologic structures. The PFSA approach, however, is able to compare the protein structures with diverse homology, and produces the realistic outcome reflecting the difference of structural homology. A set of proteins with diverse degrees of homology is compared and the structural similarity is assessed.
In this study, with the SCOP classification as a gold standard, the proteins with different homology are compared to validate that the distribution of PFSA-S values makes the sense with protein classification.
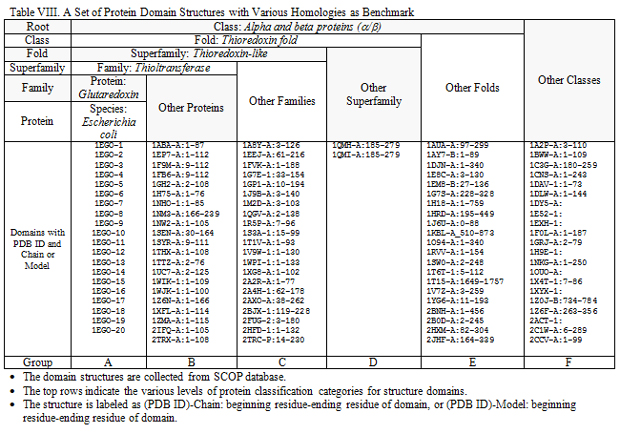
With diverse degree in structural homology, a library of 106 protein structures as a benchmark is shown in Fig. 3 and listed in Table VIII.
All protein domain structures are compared with the first conformer of 1EGO-1, and each pair of comparison generates the PFSA-S to specify the structural similarity. In order to assess the score of structural similarity between 1EGO-1 and various protein domains, all of values of PFSA-S are display in Fig. 4, where the values of PFSA-S are distributed in the order of columns same as in Table VIII. A polynomial trend line is plotted in Fig. 4. Although few of PFSA-S values show false positive or false negative, in overall, the most of values of PFSA-S for comparison of various homologous proteins are coherent with the structure classification of protein (SCOP).
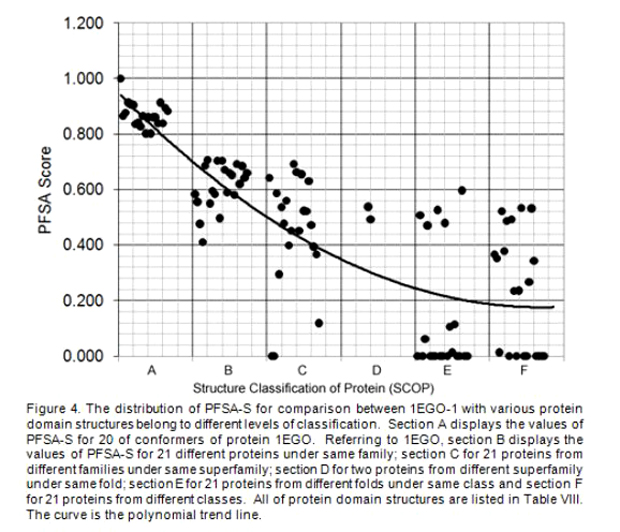
The PFSA approach demonstrates a new prospect for protein structure comparison. A consistent procedure for protein structure comparison is adopted in the PFSA approach. The PFSA approach provides the PFSA-S for quantitative measurement of similarity for global structural comparison, and it offers the PFSA alignment table for qualitative examination of local structures.
References:
- Yang J. Comprehensive description of protein structures using protein folding shape code. Proteins 2008;71.3:1497-1518
- Yang J: Complete Description of Protein Folding Shapes for Structural Comparison. In: Series: Protein Biochemistry, Synthesis, Structure and Cellular Functions: Protein Folding. Edited by Walters EC. New York, Nova Science Publishers, (ISBN: 978-1-61761-259-6), 2011, 421-442
- Yang J & Lee WH, Protein Structure Alphabetic Alignment, Protein Structure, Edited by Eshel Faraggi, InTech Publishers, (ISBN 978-953-51-0555-8), 2012, 133-156
