- Conformation Analysis
- Protein Structure Alignment
- Protein Misfolding vs. Alzheimer Disease
- Fragment Search
- Evaluate Structural Similarity for Proteins with Diverse Degrees in Homology
- Mutation Analysis
- Analysis of CDR Loops in Antibody
- Comparison of Insulin Receptor vs. IGF-1 Receptor
- Drug Binding Site
- Predicting Off Target Hits in Drug Discovery
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
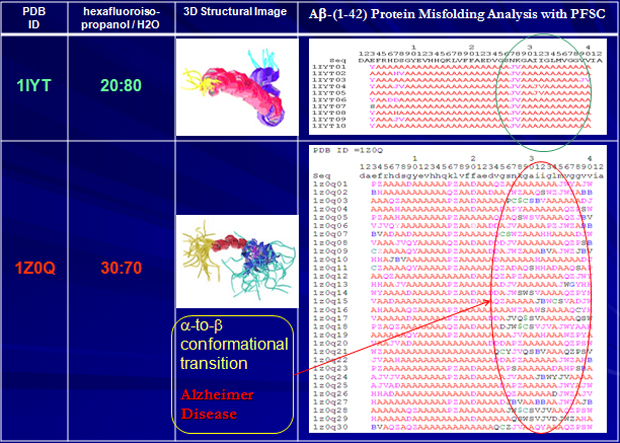
Protein Misfolding vs. Alzheimer Disease
Alzheimer Disease & Amyloid Beta-(1-42) Peptide
- The major components of neurotic plaques found in Alzheimer Disease (AD) are peptides known as amyloid beta-peptides (A-beta-42).
- In vitro amyloid beta-peptides may undergo a conformational transition from a soluble form to aggregated fibrillary b-sheet structures, which seem to be neurotoxic.
- Conformational studies on these peptides in aqueous solution are complicated by their tendency to aggregate.
- Compare the NMR conformers of A-beta-(1-42) of 1Z0Q and 1IYT in aqueous media to reveal the misfolding, alpha-to-beta conformational transition
Reference:
- Orlando Crescenzi, Simona Tomaselli, Remo Guerrini, Severo Salvadori, Anna M. D’Ursi, Piero Andrea Temussi and Delia Picone, Solution structure of the Alzheimer amyloid b-peptide (1–42) in an apolar microenvironment, 2002; Eur. J. Biochem. 269,5642–5648.
- .Simona Tomaselli, Veronica Esposito, Paolo Vangone, Nico A. J. van Nuland, Alexandre M. J. J. Bonvin, Remo Guerrini, Teodorico Tancredi, Piero A. Temussi, and Delia Picone,The a-to-b Conformational Transition of Alzheimer’s Ab-(1–42) Peptide in Aqueous Media is Reversible: A Step by Step Conformational Analysis Suggests the Location of b Conformation Seeding, 2006;ChemBioChem, 7, 257 – 267.
